728x90
- 람다식(Ramdba)
- 익명 메소드
- 메소드와 동일하게 입력(파라미터), 출력(리턴)
- 문법 : (매개변수) => { 함수 내부(식) };
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _120_Ramdba
{
delegate void dPrint(string str);
delegate int dAdd(int a);
class Program
{
static public void CallPrint(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
static public int CallAdd(int a)
{
return a + a;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
dPrint dp = CallPrint;
dp("CallPrint");
dp = (str) => { Console.WriteLine(str); };
dp("Ramdba");
dAdd da = CallAdd;
Console.WriteLine("CallAdd : " + da(10));
da = (a) => { return a + a; };
Console.WriteLine("Ramdba : " + da(10));
}
}
}
- 리스트와 람다식
- 리스트 함수 중 delegate 파라미터
- Collections에서 다양하게 활용
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _121_ListRamdba
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
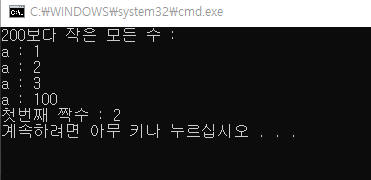
List<int> listData = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3, 100, 200, 300 };
//public delegate bool Predicate<in T>(T obj);
//public List<T> FindAll(Predicate<T> match);
List<int> listfindAll = listData.FindAll((num) => { return num < 200; }); //(num) => num < 100
Console.WriteLine("200보다 작은 모든 수 : ");
foreach(int a in listfindAll)
{
Console.WriteLine("a : " + a);
}
int findNum = listData.Find((num) => num % 2 == 0);
Console.WriteLine("첫번째 짝수 : " + findNum);
}
}
}
- 함수와 람다식
- 함수의 파라미터
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _122_FuncRamdba
{
delegate void dPrint(string str);
delegate void dFunc();
class Program
{
static public void CallPrint(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
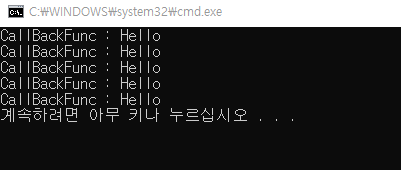
static public void CallBackFunc(dPrint dp, string msg)
{
if (null != dp)
dp("CallBackFunc : " + msg);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
CallBackFunc(CallPrint, "Hello"); //함수 연결
CallBackFunc(delegate (string str) { Console.WriteLine(str); }, "Hello"); //delegate 직접
CallBackFunc((string str) => { Console.WriteLine(str); }, "Hello"); //람다의 식형태
CallBackFunc((str) => Console.WriteLine(str), "Hello"); //람다식 기본
CallBackFunc(str => Console.WriteLine(str), "Hello");
dFunc dfunc = () => Console.WriteLine("No Params"); //파라미터가 없는 경우 () 반드시 사용
}
}
}
- Action과 Func
- Action : 리턴값이 없는 경우(void)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _123_Action
{
class Program
{
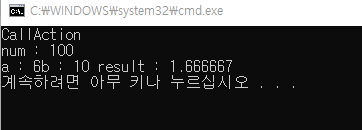
static void CallAction()
{
Console.WriteLine("CallAction");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Action aFunc;
Action<int> aFunc2;
Action<float, int> aFunc3;
aFunc = CallAction;
aFunc2 = (num) => Console.WriteLine("num : " + num);
aFunc3 = (a, b) =>
{
float result = b / a;
Console.WriteLine("a : " + a + "b : " + b + " result : " + result);
};
aFunc();
aFunc2(100);
aFunc3(6.0f, 10); // 10/6
}
}
}
- Func : 리턴값이 있는 경우
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _124_Func
{
class Program
{
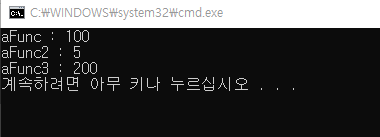
static int CallFunc()
{
return 100;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Func<int> aFunc;
Func<int, float> aFunc2;
Func<int, int, int> aFunc3;
aFunc = CallFunc;
aFunc2 = (int a) => { return (float)(a / 2.0f); };
aFunc3 = (a, b) => (a + b);
Console.WriteLine("aFunc : " + aFunc());
Console.WriteLine("aFunc2 : " + aFunc2(10));
Console.WriteLine("aFunc3 : " + aFunc3(100, 100));
}
}
}
728x90
'게임 프로그래밍 > C#' 카테고리의 다른 글
| C# 파일 처리 Stream, System.IO (0) | 2021.12.23 |
|---|---|
| C# LINQ(Select, Oderby, Group, Join) (0) | 2021.12.21 |
| C# 대리자 delegate & 이벤트 event (0) | 2021.12.21 |
| C# 예외 처리(try~catch, exception, throw, finally) (0) | 2021.12.21 |
| C# 함수/클래스 일반화(Generic 제네릭) (0) | 2021.12.20 |

